What is 4D BIM and how is it used to enhance construction planning?
4D BIM Simulation for LTA Rail Project in Singapore
The integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) in construction management has the potential to provide project managers with advanced digital tools for planning, designing, and executing construction projects. Among the various dimensions of BIM, 4D BIM incorporates time as the fourth dimension. Combining a BIM model with a project plan creates a powerful simulation that can guide the project delivery process effectively.
This article delves into how 4D BIM is utilized in construction planning, serving as a guide for project managers and contractors interested in incorporating it into their project delivery workflow.
Use Cases of 4D BIM
4D BIM, or four-dimensional Building Information Modeling, integrates project scheduling and timeline management into the construction process. Here are several key use cases:
1. Construction Planning and Scheduling
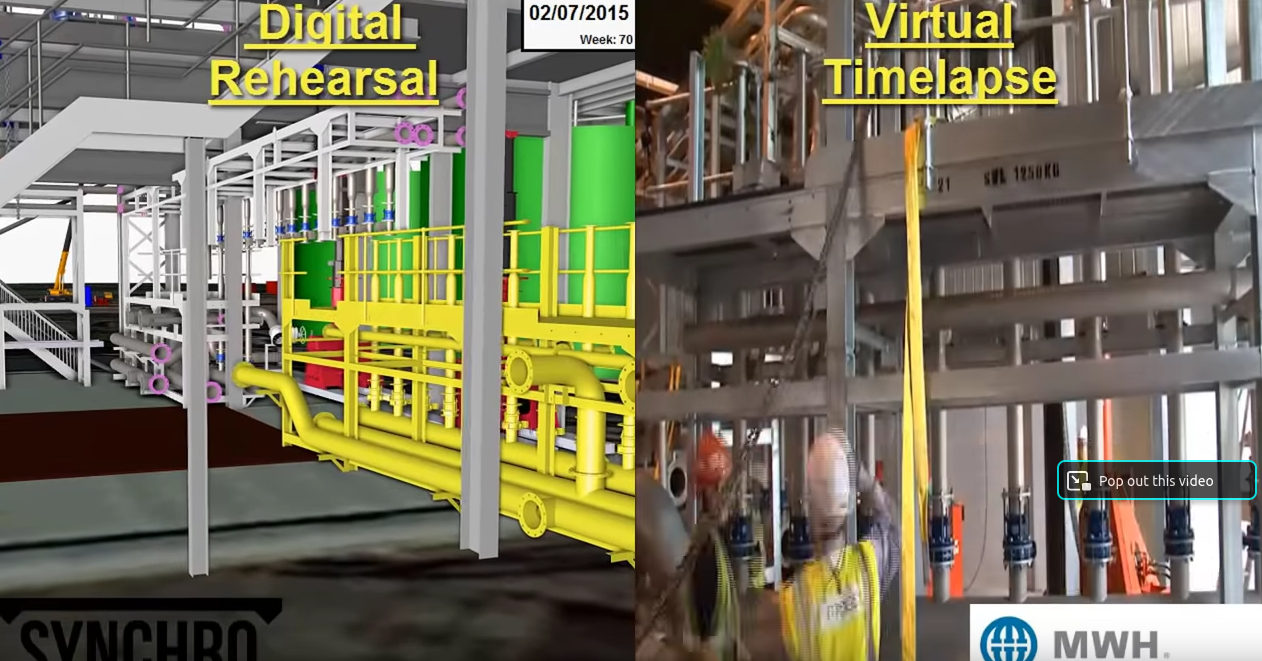

- Visual Scheduling: Link project timelines to the BIM model, visualizing construction sequences and identifying the most efficient workflow.
- Simulation of Construction Sequences: Simulate the construction process to plan and optimize the order of operations, reducing conflicts and downtime.
2. Resource Management
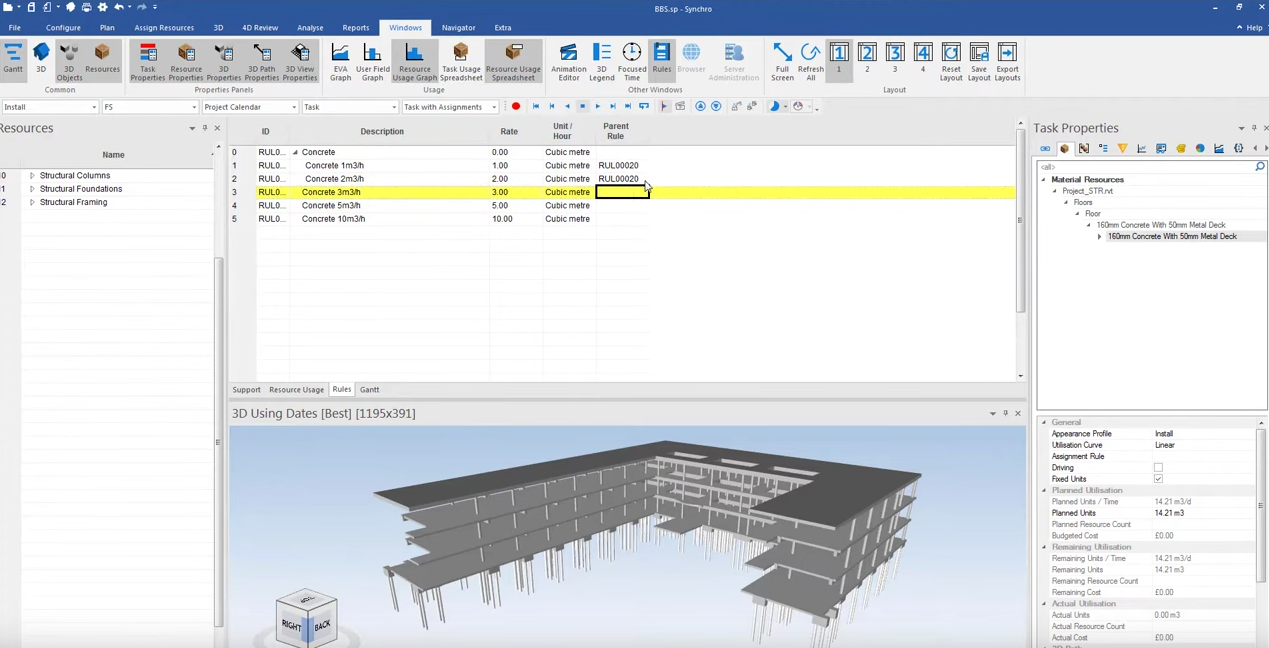
- Labor and Equipment Allocation: Plan and optimize the allocation of labor and equipment over the project timeline to ensure efficient utilization. The allocation of time and materials to the BIM model is modelled by the BIM team at the start of the project.
- Material Logistics: Schedule deliveries and manage storage of materials on-site to avoid delays and minimize storage costs.
3. Clash and Conflict Detection
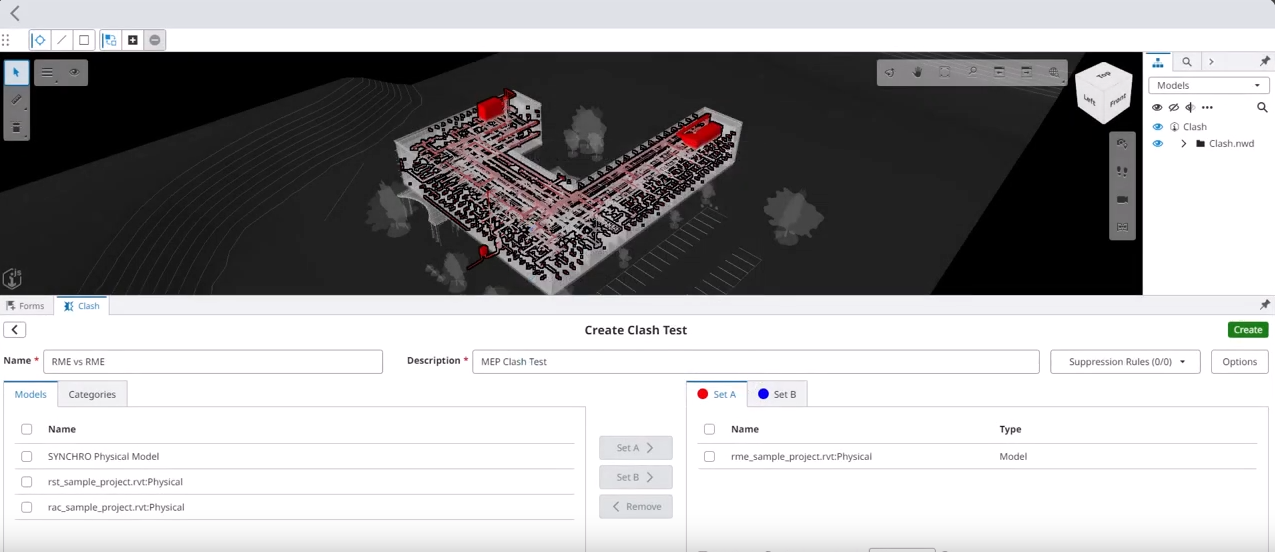
- Clash Detection: Identify and resolve potential clashes not only in space (3D) but also in time (4D), preventing schedule delays caused by conflicts. The 4D plan should be continuously updated to keep track of potential clashes.
- Pre-construction Issue Identification: Identify and solve issues before construction begins, reducing the need for costly changes and rework.
4. Stakeholder Communication and Coordination
- Enhanced Communication: Use visual timelines and simulations to communicate plans and schedules to stakeholders, improving understanding and collaboration.
- Coordination Among Contractors: Facilitate coordination among various contractors and subcontractors, ensuring everyone is aligned with the project timeline.
5. Risk Management
- Schedule Risk Analysis: Identify potential risks to the project schedule and develop mitigation strategies.
- Impact Analysis: Assess the impact of potential changes or delays on the project schedule, helping to manage and mitigate risks.
6. Progress Monitoring and Control

- Real-time Progress Tracking: Compare actual progress against the planned schedule, identifying deviations and enabling timely corrective actions.
- Performance Analysis: Analyze the performance of different phases of the construction process to identify areas for improvement in future projects.
7. Safety Management
- Safety Planning: Plan and visualize safety measures in the context of the overall project timeline, enhancing on-site safety.
- Work Zone Management: Manage and schedule work zones to minimize overlap and reduce the risk of accidents.
Key Challenges
Despite its significant benefits, the implementation of 4D BIM in construction projects comes with its own set of challenges. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for maximizing the potential of this advanced technology. Here are some of the top challenges faced in implementing 4D BIM:
- Skill and Knowledge Gap: The successful implementation of 4D BIM requires skilled professionals with expertise in both BIM software and project scheduling. However, there is often a shortage of trained personnel proficient in utilizing 4D BIM tools effectively. A skilled team should combine project planning capabilities alongside BIM modelling and management expertise.
- Cost and Investment: Implementing 4D BIM involves upfront costs associated with software licenses, training, and hardware infrastructure. For smaller firms or projects with tight budgets, the initial investment in 4D BIM technology may pose a barrier to adoption.
- Change Management: Introducing new technologies and workflows, such as 4D BIM, often requires a cultural shift within organizations. Resistance to change from stakeholders accustomed to traditional methods of project management and planning can impede the adoption of 4D BIM.
- Data Quality and Consistency: The accuracy and consistency of data inputs play a crucial role in the effectiveness of 4D BIM simulations. Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to flawed scheduling, clashes, and delays during construction. Ensuring data quality through standardized processes, validation checks, and continuous data updates is essential for reliable 4D BIM modeling.
Working with a BIM service provider can be a quick way to realize the benefits of 4D BIM on your first project, eliminating the need for extensive retraining and coordination among multiple stakeholders.
How to implement 4D BIM
In a typical design-bid-build contract, engineering consultants collaborate with architects to develop an initial design for the project. Throughout this process, the contractor may or may not have access to BIM models being generated. If not provided, the contractor would need to convert the 2D drawings into BIM format to integrate the time elements of the project plan into their BIM models. Where detailed BIM models do not yet exist, it helps to know that a low Level of Development (LOD 300) model is often sufficient for creating the 4D model.
In projects involving specialized equipment, such as industrial plants, renewable energy installations, and complex rail projects, obtaining BIM models from equipment manufacturers is ideal. By incorporating these manufacturer-provided BIM models into the 4D BIM environment, project teams can coordinate the installation sequence of equipment alongside other construction activities, optimizing spatial utilization and ensuring efficient workflow management. These detailed BIM objects can be included into the 4D BIM later on in the construction phase.
In most scenarios, professional planners are engaged to create a project schedule. Common software utilized by the construction industry for project plans includes Microsoft Project or Oracle Primavera P6 for large scale infrastructure projects. These program plans can be imported directly into BIM simulation software like Synchro 4D. Our project BIM managers will integrate the project plan with the BIM models, enabling the creation of a Synchro 4D simulation.
Deliver 4D BIM with Bimeco
4D BIM enhances project management by integrating scheduling and timeline management with BIM models. These models serve various purposes, such as planning the project sequence, anticipating safety risks during project delivery, and visualizing the installation sequences of complex equipment during construction.
Incorporating a 4D BIM model into concurrent engineering sessions effectively engages project stakeholders, offering project managers and BIM managers a valuable project management tool. The ease in which a layperson can understand the visual project sequence will ultimately help project managers reap operational and time-saving efficiencies during the project.
