How Is BIM Used in Plumbing & Sanitary Projects in Construction?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing the construction industry by enhancing efficiency, precision, and collaboration. When it comes to plumbing and sanitary projects, BIM offers substantial benefits that improve planning, design, installation, and maintenance processes. Here's a closer look at how BIM is used in plumbing and sanitary projects within the construction sector.
1. Precise 3D Modeling of Plumbing Systems
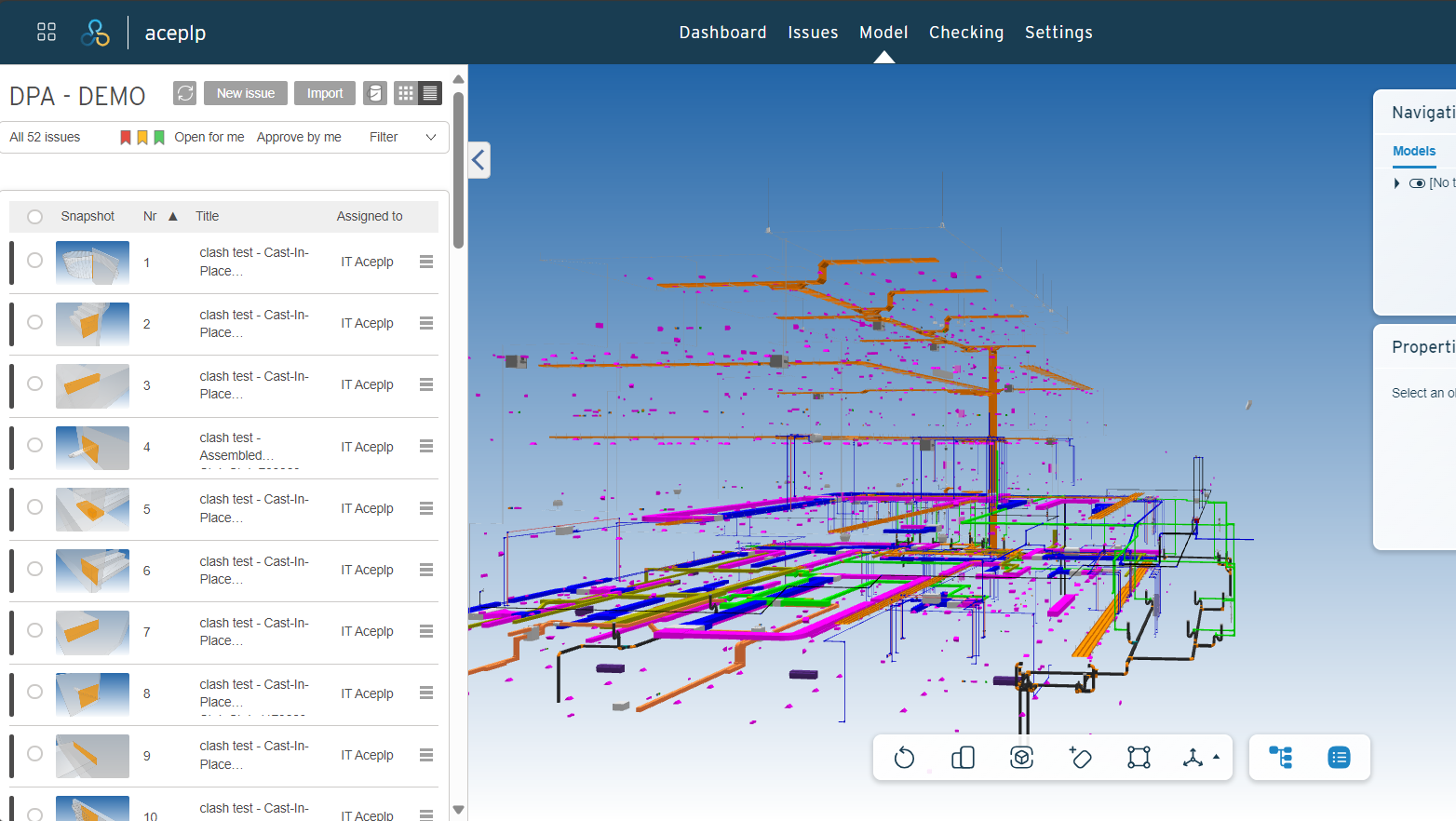
BIM enables the creation of highly accurate 3D models of plumbing and sanitary systems. These models provide a detailed representation of pipes, fixtures, drainage, and water supply systems. Through these visualizations, designers can better understand the spatial arrangement and identify potential clashes with other building systems, such as HVAC or structural components.
Example: A detailed BIM model allows engineers to verify that pipes don’t interfere with beams or ducts, minimizing rework and errors on-site.
2. Clash Detection and Coordination
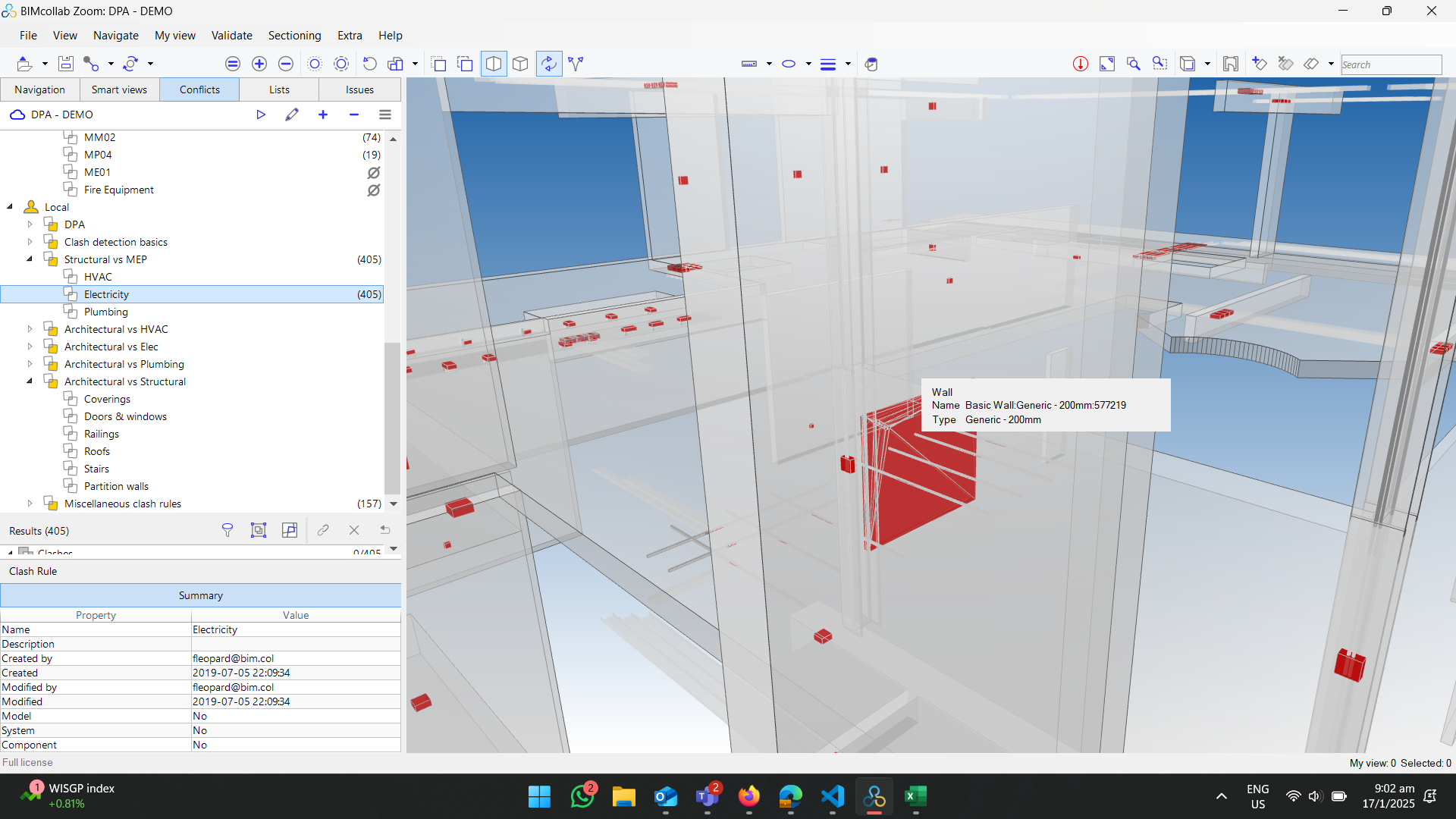
One of BIM’s standout features is its clash detection capability. For plumbing and sanitary projects, this is crucial because these systems often intersect with other critical infrastructure, such as electrical wiring and HVAC ducts.
Using BIM, potential conflicts can be identified and resolved during the design phase, reducing costly delays and on-site adjustments.
Benefit: Smooth coordination between various disciplines ensures that plumbing and sanitary systems are seamlessly integrated into the overall building structure.
3. Accurate Quantity Takeoff and Cost Estimation
BIM provides detailed material schedules and quantity takeoffs for plumbing and sanitary components, such as pipes, valves, fittings, and fixtures. This data enables more precise cost estimation and budgeting for the project.
Time-Saving Advantage: By automating the process of material calculation, BIM reduces human error and accelerates project timelines.
4. Enhanced Collaboration Among Stakeholders
BIM fosters collaboration by offering a single source of truth for all project stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and plumbers. Through cloud-based BIM platforms, teams can share updates, review changes, and coordinate installations in real time.
Impact: Collaboration ensures that the plumbing design aligns with client requirements, local codes, and sustainability goals.
5. Design Optimization for Water Efficiency
BIM aids in designing plumbing systems that prioritize water conservation. Engineers can simulate water flow, pressure, and drainage to optimize system efficiency. This is especially important in green building projects that aim to meet GREENMARK, LEED, or other sustainability certifications.
Simulation Tools: By analyzing water usage patterns, BIM helps in selecting appropriate fixtures and pipe sizes, reducing wastage and energy consumption. These reports can be extracted as supporting documentation for sustainability certifications like LEED.
6. Facilitating Prefabrication
BIM supports prefabrication of plumbing components by providing precise measurements and fabrication drawings. In a Design for Manufacturing & Assembly workflow, 2D drawings are extracted from BIM models. Additional fabrication details are recorded in the 2D drawings to capture the intricacies of the fabrication process.
By doing so, contractors can prefabricate sections of plumbing systems off-site, reducing installation time and improving quality control.
Advantage in Complex Projects: Prefabrication is particularly beneficial in large-scale or multi-floor buildings where modular assemblies streamline installation.
7. Lifecycle Management and Maintenance
BIM models are not just useful during the construction phase but also throughout the lifecycle of a building. For plumbing and sanitary systems, BIM serves as a digital twin, providing valuable information for maintenance and future upgrades.
Example: Facility managers can use BIM data to locate pipes, valves, or fixtures without invasive inspections, saving time and reducing disruptions.
8. Compliance with Building Codes and Standards
BIM incorporates regional plumbing codes and standards, ensuring that the design complies with legal and safety requirements. Automatic code-checking features help identify any violations early in the design process.
Result: This reduces the risk of regulatory delays and ensures that the plumbing system meets all necessary criteria.
Conclusion
BIM has become an indispensable tool in plumbing and sanitary projects within construction. From precise 3D modeling and clash detection to lifecycle management and sustainability, BIM streamlines every stage of the project. By embracing BIM, stakeholders can deliver plumbing systems that are efficient, cost-effective, and compliant with industry standards, ultimately enhancing the quality and performance of construction projects.
Whether you’re a contractor, designer, or facility manager, integrating BIM into your plumbing and sanitary workflows is a step toward smarter and more sustainable construction.
