What is Virtual Design and Construction?

In the evolving landscape of global construction, Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) has emerged as a pivotal technology, promising to revolutionize the way buildings are designed, constructed, and maintained. Particularly in Singapore, a nation known for its innovative approaches to urban development and sustainability, VDC is becoming an indispensable tool in overcoming the unique challenges faced by the construction sector.
Understanding Virtual Design and Construction (VDC)
Definition and Key Components of VDC
At its core, VDC is a management approach that integrates multi-disciplinary performance models of design-construction projects, including the Product (what we build), Work Processes (how we build), and Organization of the design - construction - operation team (who does the work) to support explicit and public business objectives. This approach is underpinned by three key components: Building Information Modeling (BIM)*, integrated project delivery (IPD), and advanced communication tools, all of which work together to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of construction projects.
The Process of VDC
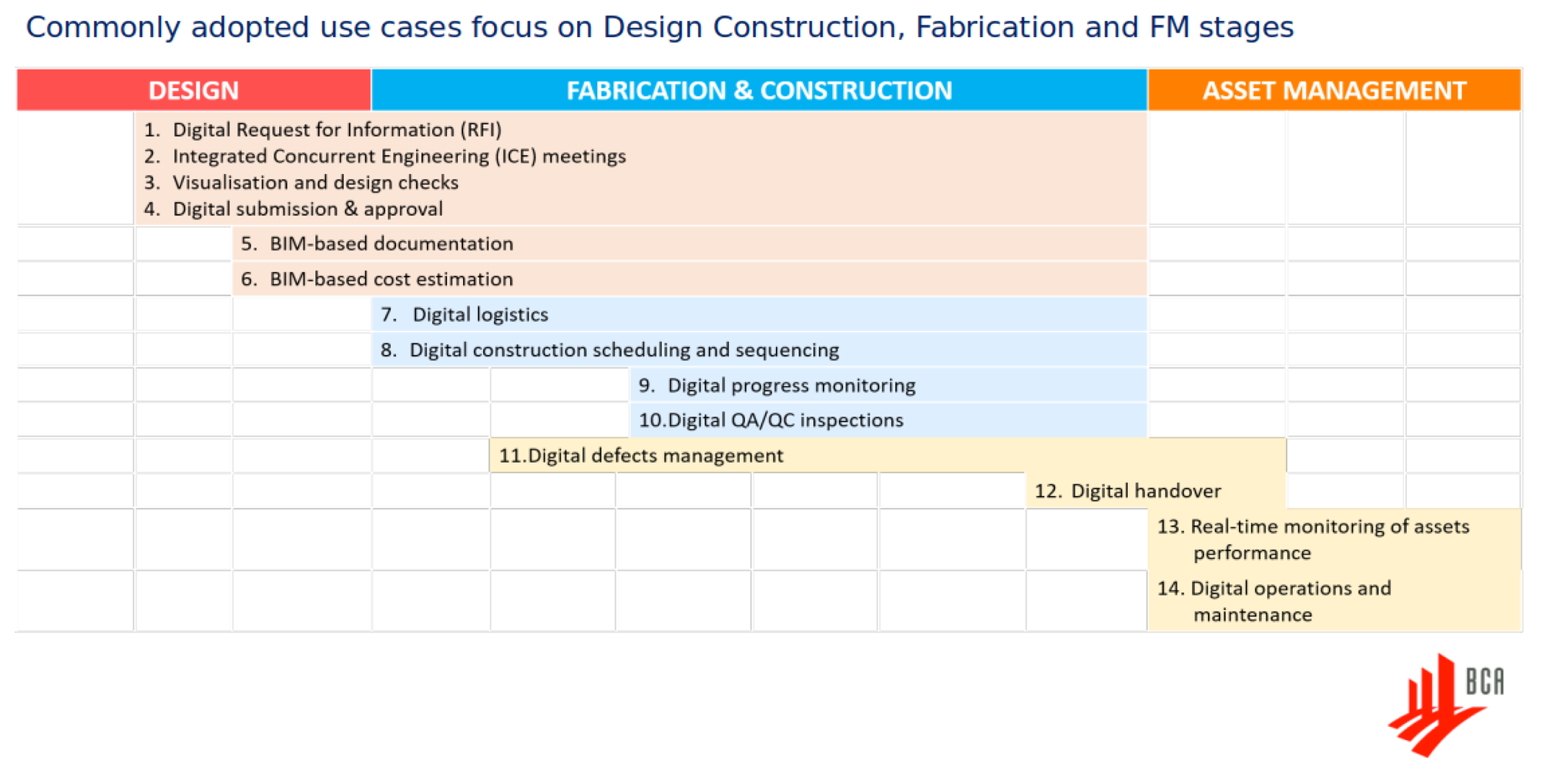
The VDC process encompasses the entire lifecycle of a construction project. During the planning and design phase, VDC enables the creation of digital twins of buildings, allowing for thorough analysis and optimization of designs. In the construction phase, these models facilitate precise and efficient building methods, while in the operations and maintenance phase, they provide detailed information to support building management.
Benefits of VDC
The adoption of VDC offers a myriad of benefits, including improved project visualization, which helps in identifying potential issues early on; enhanced collaboration and communication among stakeholders; significant cost savings and efficiency improvements; and a reduction in errors and rework, thanks to the accurate and detailed planning enabled by VDC.
The Significance of VDC in Singapore
The Construction Industry in Singapore
Singapore’s construction industry faces several challenges, including a persistent labor shortage, the high cost of construction, and ambitious sustainability goals. VDC presents an opportunity to address these challenges head-on by streamlining project delivery, reducing the need for physical labor, and improving the sustainability of construction practices.
The Role of Government and Industry Bodies
The Singaporean government, along with industry bodies such as the Building and Construction Authority (BCA) of Singapore, has been instrumental in promoting the adoption of VDC and related technologies.
Initiatives such as the BIM Roadmap, launched in 2010, aim to improve the construction sector's productivity and sustainability by encouraging the use of digital tools in construction projects. The mandatory use of Building Information Modelling (BIM) for construction projects exceeding 5000 square meters, highlights Singapore's commitment to integrating digital tools into construction workflows.
BCA has implemented several initiatives to support the construction sector, particularly by facilitating connections between industry players and shared services providers. One of the platforms for this purpose is the Shared Services Programme administered by the Specialists Trade Alliance of Singapore (STAS). This program aims to serve the Integrated Digital Delivery (IDD) procurement needs of stakeholders in the Built Environment sector, including consultants, builders, specialist contractors, and suppliers, thereby supporting the Industry Transformation Map (ITM) for the Built Environment
Implementing VDC in Singapore: Case Studies and Success Stories
Case Studies of VDC Projects in Singapore
Singapore has seen several successful implementations of VDC. Projects like the Marina Bay Sands and the Jewel Changi Airport have utilized VDC to achieve remarkable outcomes in terms of efficiency, cost, and sustainability. These projects serve as benchmarks, demonstrating the tangible benefits that VDC can bring to complex construction projects.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
The success of VDC in Singapore underscores the importance of early adoption and the integration of VDC principles throughout the project lifecycle. Best practices include investing in training for project teams, fostering collaboration among stakeholders, and leveraging VDC for sustainability.
Challenges and Opportunities for VDC in Singapore
Overcoming Barriers to Adoption
Despite its benefits, the adoption of VDC in Singapore faces hurdles such as cultural resistance, the need for substantial training, and the initial investment costs. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from both the government and the private sector, including incentives for adoption, and educational programs to build a skilled workforce.
Future Opportunities and Trends
Emerging technologies such as AI, VR/AR, Digital Twins, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are set to enhance the capabilities of VDC further, offering new opportunities for innovation in construction. Moreover, VDC is poised to play a critical role in supporting Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative and achieving its sustainability goals.
The Road Ahead for VDC in Singapore
The strategic importance of VDC for future projects in Singapore cannot be overstated. As the construction industry continues to evolve, VDC offers a pathway to more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable construction practices.
