Creating BIM Digital Twins for Operations & Facility Management
In this article, we'll explore how a BIM model can be developed into a Digital Twin for Operations and Facility Management (FM), providing real-world insights to its benefits and use-cases.

In the evolving landscape of construction and facility management, the transition from Building Information Modeling (BIM) to Digital Twins is transforming how we manage and operate buildings. This transition offers opportunities for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing the overall lifecycle of a facility. In this article, we'll explore how a BIM model can be developed into a Digital Twin for Operations and Facility Management (FM), providing real-world insights to its benefits and use-cases.
What is a BIM Model?
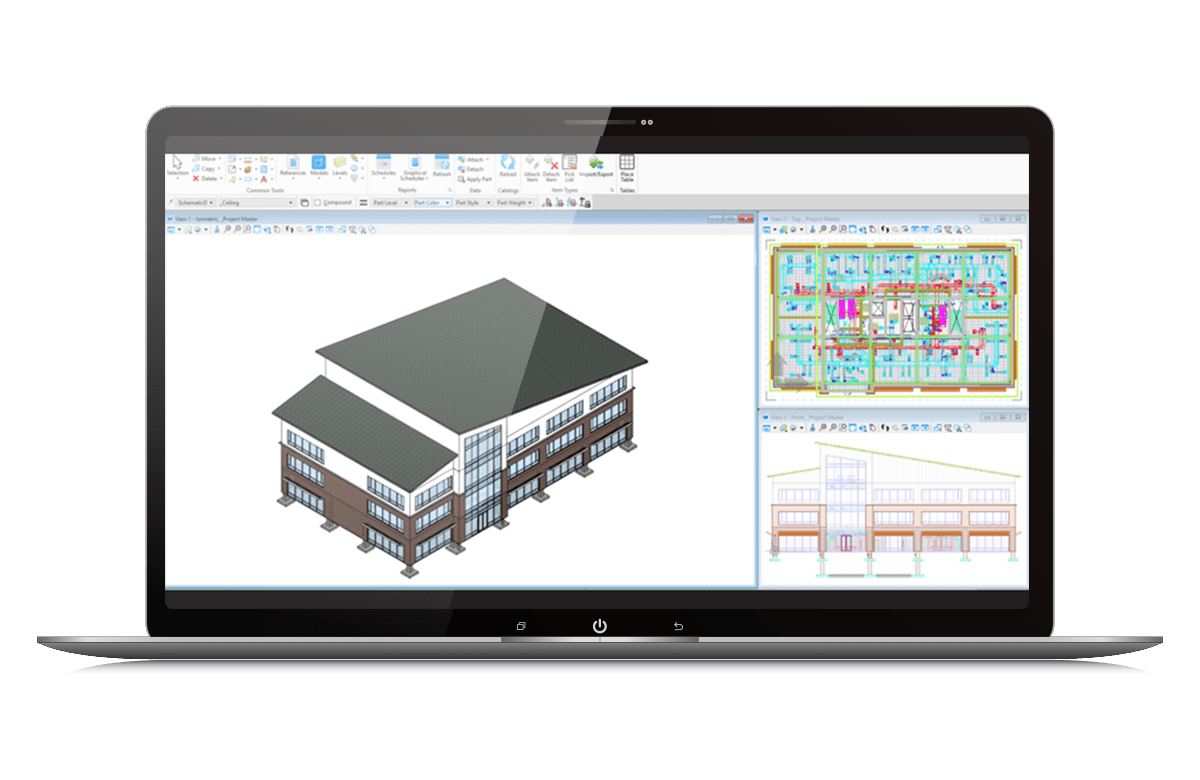
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility. It serves as a shared knowledge resource, providing detailed information throughout the lifecycle of a building, from design and construction to maintenance and operations. BIM encompasses various dimensions, including 3D models, time (4D), cost (5D), and more, making it an essential tool for architects, engineers, and construction professionals.
Understanding Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object or system, replicating its behavior throughout its entire lifecycle. By utilizing real-time data from sensors on the physical asset, digital twins simulate and monitor operations, providing a dynamic model that evolves with the object. This technology can be applied to various scales, from individual equipment in a factory to large installations like wind turbines or even entire cities. Digital twins enable more effective oversight of asset performance, early identification of potential issues, and informed decision-making for maintenance and lifecycle management.
Steps to Creating a Digital Twin from BIM
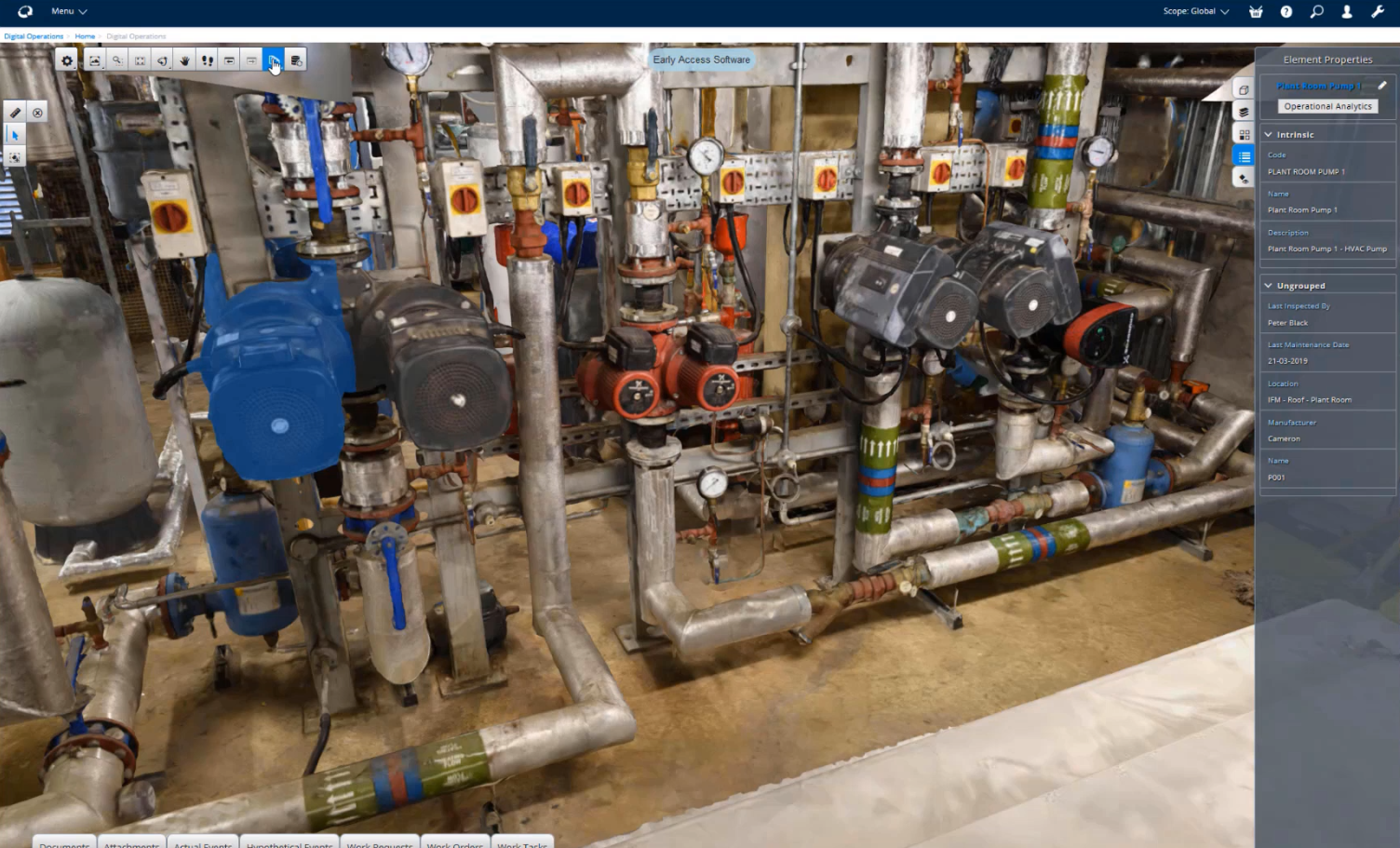

1) Identify Critical Use Cases
Determine the most valuable applications for your digital twin by focusing on high-ROI use cases. Examples include predictive maintenance, energy optimization, enhanced facility management, and safety monitoring. Clearly define the objectives and data requirements for each use case to guide the digital twin's development.
2) Creating the Visual Context
Develop a detailed BIM model that accurately represents the physical asset. Work closely with the BIM team to ensure the model is up-to-date and capable of integrating real-time operational data. If the model is large or complex, consider exporting it to a web-compatible format like glTF to facilitate smoother visualization and interaction.
3) Bringing Operational Data into the Visual Context
Select and deploy sensors strategically to capture relevant real-time data that aligns with the visual context provided by the BIM model. Utilize cloud-based platforms like AWS IoT Core and AWS IoT SiteWise to bring sensor data from edge devices into the cloud, ensuring seamless integration with the visual model. Regularly calibrate sensors and update the BIM model to maintain accuracy.
4) Performing Simulation & Analysis from Stored Data
Use the integrated operational and visual data to perform simulations and analyses that provide actionable insights. Implement predictive analytics and other advanced tools to forecast maintenance needs, optimize operations, and detect anomalies. Continuous monitoring and refinement of the digital twin will ensure it remains a valuable tool for decision-making and asset management.
Benefits of Transitioning to a BIM Digital Twin
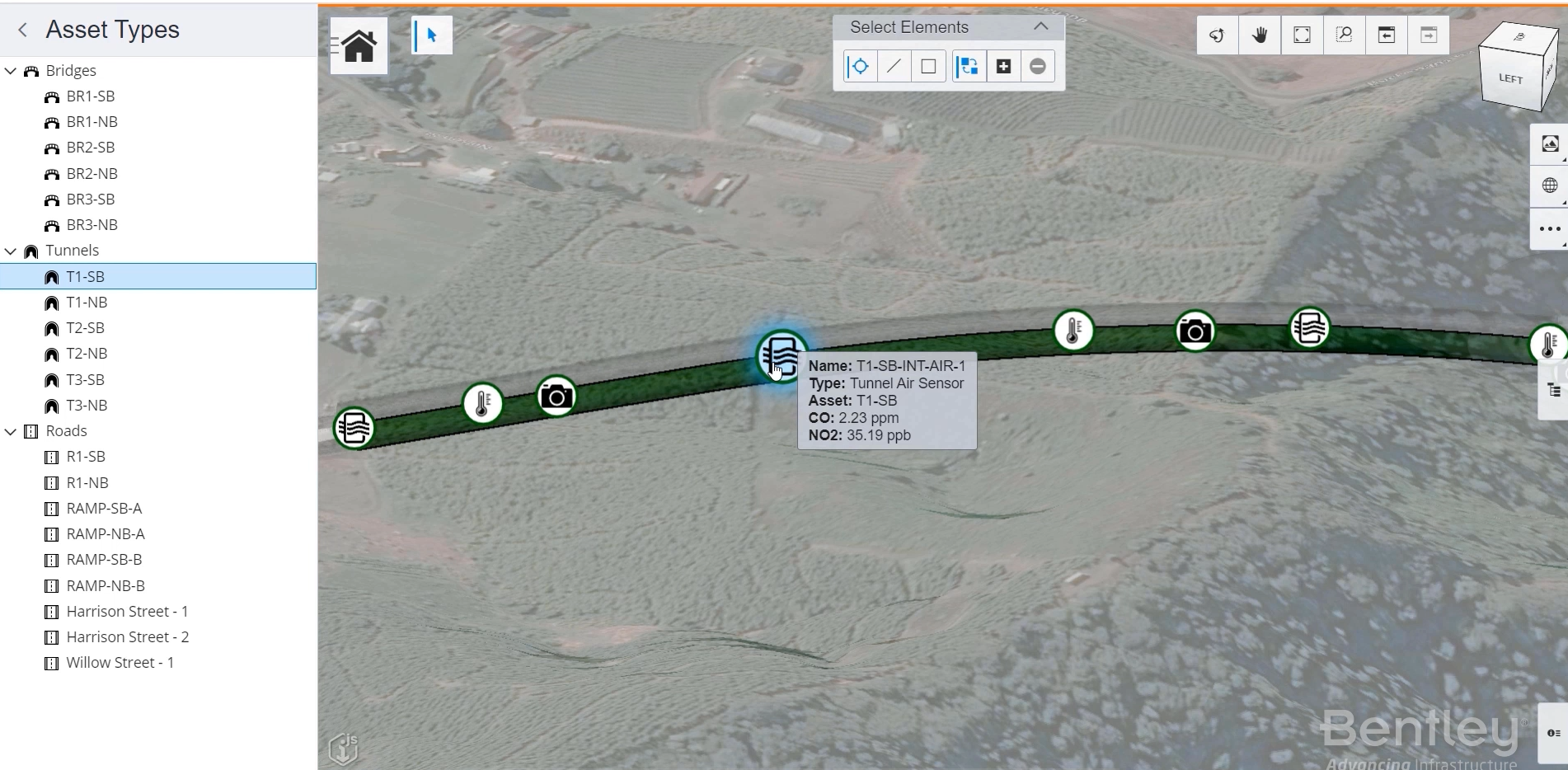
Transitioning from a BIM model to a Digital Twin provides significant advantages for Operations and Facility Management. With most modern buildings designed and constructed using BIM, these models can be effectively repurposed as Digital Twins, unlocking new opportunities for enhanced management and operational efficiency.
Improved Asset Performance with Real-time Analytics
Digital twins offer real-time insights that optimize the performance of equipment, plants, and facilities. In healthcare, digital twins create virtual models of hospitals, labs, and other facilities. These models monitor crucial ambient metrics like temperature, air quality, and humidity, which can significantly impact patient outcomes. In such critical environments, maintaining a log of ambient data is essential for meeting stringent regulatory requirements.
Predictive Capabilities for Maintenance
Digital twins offer a comprehensive visual and digital overview of your manufacturing plant, commercial building, or facility, even when composed of thousands of components. Smart sensors continuously monitor each element's output, flagging issues or faults as they occur. This allows you to take proactive measures at the first sign of trouble, preventing equipment failures before they happen.
Digital twins are widely used in the energy sector to support strategic project planning and optimize the performance and lifecycles of existing assets, such as offshore installations, refining facilities, wind farms, and solar projects. When a digital twin predicts a component failure, maintenance can be scheduled during low-impact periods, preventing costly downtime.
Maintenance workflows are significantly improved when Digital Twins are integrated with BIM. In a 6D BIM model, additional asset information—such as maintenance schedules and product specifications—can be referenced alongside real-time sensor data, providing a comprehensive view for efficient management.
Remote Monitoring
The virtual nature of digital twins allows for remote monitoring and control of facilities, reducing the need for on-site personnel. This also enhances safety by minimizing the need for staff to interact with potentially hazardous industrial equipment.
Innovative asset operators are using digital twins to drive new business models, enabling them to provide shared services across multiple assets. Digital twins allow for remote monitoring and the efficient dispatch of personnel when issues arise. Additionally, they offer valuable site context which assets operators can use to train their service personnel, reducing time-to-recovery for equipment failures.
Deliver Ahead of Schedule
Digital twins enable you to accelerate production timelines by creating digital replicas of products and facilities before they are physically built. By simulating scenarios, you can observe how your product or facility responds to failures and make necessary adjustments before moving into actual production.
Begin Your Journey from BIM to Digital Twins
Transitioning from BIM to a Digital Twin marks a significant leap in Operations and Facility Management. This process involves careful coordination of several components, from preparing the visual model and integrating physical sensors to deploying everything in a cloud environment. Each step must be meticulously planned to ensure the digital twin functions effectively and delivers maximum value.
By integrating real-time data, enhancing decision-making, and enabling predictive maintenance, Digital Twins offer a powerful tool for optimizing building performance and reducing costs. As technology advances, Digital Twins are poised to become central to modern facility management.
Embrace the future of facility management by successfully transitioning your BIM model into a Digital Twin. By addressing each component—from visual modeling to sensor integration and cloud deployment—you can unlock the full potential of your building's operations and maintenance, setting a new standard for efficiency and innovation.
